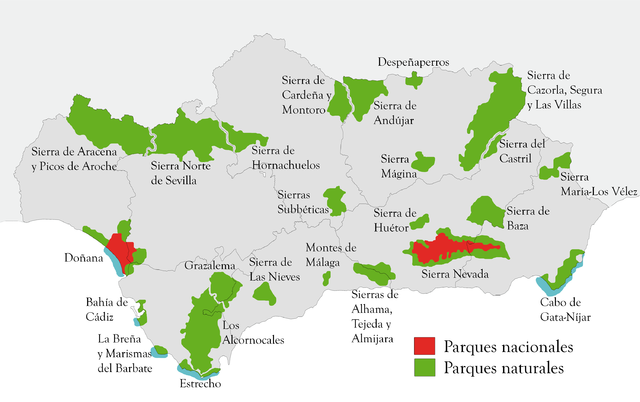
Doñana National Park (Parque nacional y natural de Doñana)
Doñana National Park is a natural reserve in Andalusia, southern Spain, in the provinces of Huelva (most of its territory), Cádiz and Seville. It covers 543 km2 (209.65 sq mi), of which 135 km2 (52.12 sq mi) are a protected area. The park is an area of marshes, shallow streams, and sand dunes in Las Marismas, the delta where the Guadalquivir River flows into the Atlantic Ocean. It was established as a nature reserve in 1969 when the World Wildlife Fund joined with the Spanish government and purchased a section of marshes to protect it. The eco-system has been under constant threat by the draining of the marshes, the use of river water to boost agricultural production by irrigating land along the coast, water pollution by upriver mining, and the expansion of tourist facilities. It is named after Doña Ana de Silva y Mendoza wife of the 7th Duke of Medina Sidonia.
Doñana National Park has a biodiversity that is unique in Europe, although there are some similarities to the Parc Naturel Régional de Camargue of the Camargue river delta in France, with which Doñana Park is twinned. The park features a great variety of ecosystems and shelters wildlife including thousands of European and African migratory birds, fallow deer, Spanish red deer, wild boars, European badgers, Egyptian mongooses, and endangered species such as the Spanish imperial eagle and the Iberian lynx.
The Doñana nature reserve includes both the Doñana National Park, established in 1969, and the Natural Park, created in 1989 and expanded in 1997, creating a buffer zone of protection under the management of the regional government. The two parks, national and natural, have since been classified as a single natural landscape. Due to its strategic location between the continents of Europe and Africa and its proximity to the Strait of Gibraltar, Doñana's large expanse of salt marsh is a breeding ground as well as a transit point for thousands of European and African birds (aquatic and terrestrial), and hosts many species of migratory waterfowl during the winter, typically up to 200,000 individuals. Over 300 different species of birds may be sighted there annually. Considered the largest nature reserve in Europe, several different scientific institutions have monitoring stations within its boundaries to ensure appropriate development of adjacent lands and conservation of the threatened species that inhabit it. The area was declared a World Heritage Site by UNESCO in 1994; in 2006 the park recorded 376,287 visitors.
During the 19th and 20th centuries, a herd of feral dromedaries roamed the area. They may have been introduced during the Moorish Conquest of Spain in the 8th century, or they may have escaped from a herd introduced by the Marquess of Molina as beasts of burden in 1829. By the 1950s, there were only eight individuals left, and these were threatened by poachers.
- 1 Geology and geomorphology
-
2
History
- 2.1 Antiquity
- 2.2 Middle Ages
- 2.3 Early modern
- 2.4 Late modern, creation of the National Park
- 2.5 Conservation
- 3 Climate
- 4 Flora
- 5 Fauna
- 6 Natural Park of Doñana: Preparque
- 7 Environmental Problems
- 8 Doñana Biological Station
- 9 Saca de las Yeguas
- 10 Other points of interest
- 11 See also
- 12 References
- 13 Further reading
- 14 External links
Links
Images Gallery
-
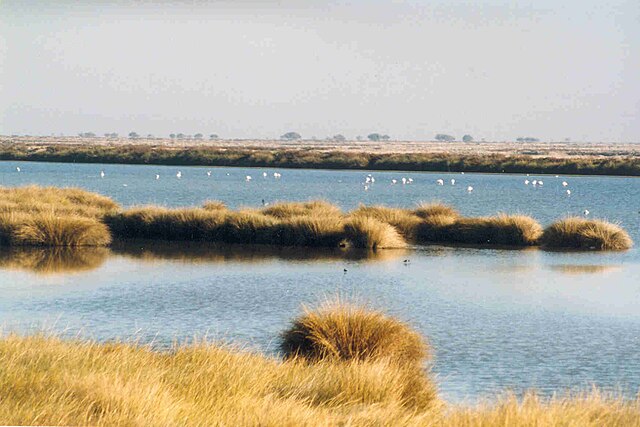

-
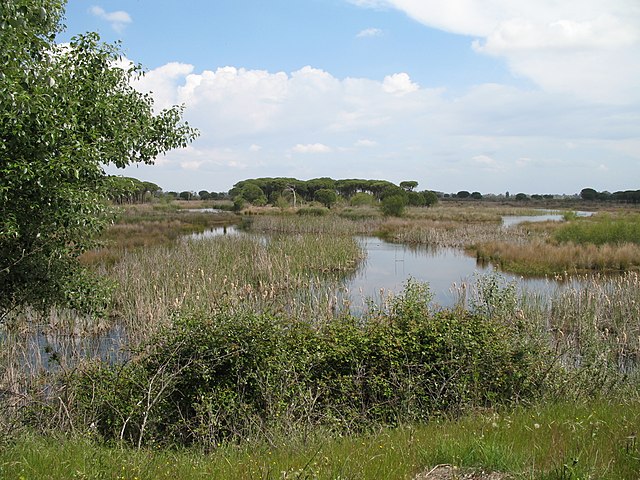 View of Doñana National Park from visitors' centre at El Acebuche
View of Doñana National Park from visitors' centre at El Acebuche
-
-
-

-

-
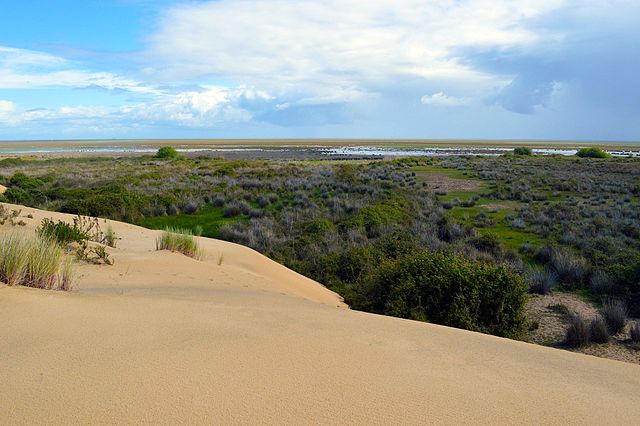
 Dunes in the park
Dunes in the park
-
 Doñana - Aerial view of Doñana National Park and surrounding areas
Doñana - Aerial view of Doñana National Park and surrounding areas
-
 Banks of the River Guadalquivir in Doñana National Park
Banks of the River Guadalquivir in Doñana National Park
-
 El Porrón observatory
El Porrón observatory
-
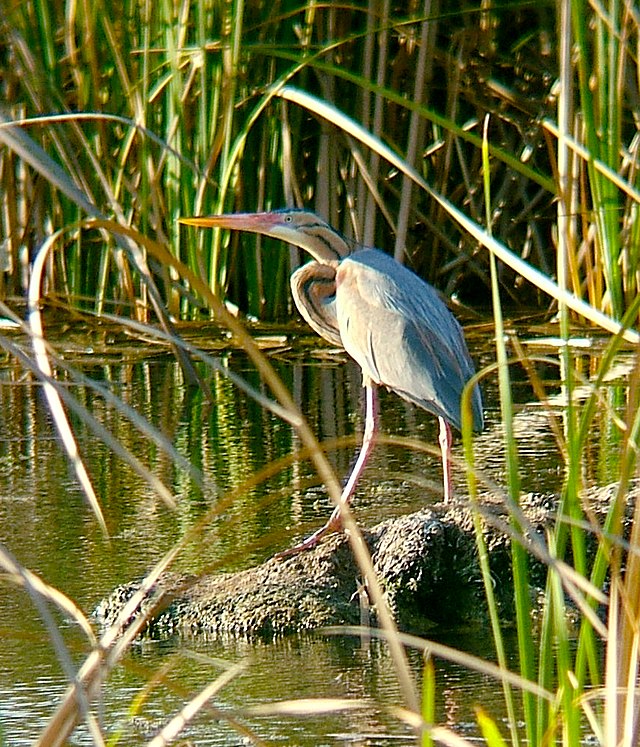 Purple heron
Purple heron
-
 Iberian lynx, one of the most emblematic species of the park
Iberian lynx, one of the most emblematic species of the park
-
 Pinar de la Algaida
Pinar de la Algaida
-
 The Port of Huelva
The Port of Huelva
-
 Rice field in Las Marismas, near Isla Mayor
Rice field in Las Marismas, near Isla Mayor
-
Wagon bearing a Simpecado (banner with insignia that proceeds images of the Holy Virgin Mary)[52] crosses the Coto Doñana on its return from the pilgrimage of El Rocío, in May 2009.
-
 Acebrón Palace (Palacio del Acebrón)
Acebrón Palace (Palacio del Acebrón)
-

-

-

-

-

-
-

-
-

-

-
-
-
-

-
-
-

-

-

-

-
-

-

-

-
-

-

-
-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-
-

-

-
-

-

-

-

-

Comments
-
Doñana National Park in Andalusia occupies the right bank of the Guadalquivir river at its estuary on the Atlantic Ocean. It is notable for the great diversity of its biotopes, especially lagoons, marshlands, fixed and mobile dunes, scrub woodland and maquis. It is home to five threatened bird species. It is one of the largest heronries in the Mediterranean region and is the wintering site for more than 500,000 water fowl each year.
2 months ago -
Marvelous area, paradise for bird watcher and not only! Many type of landscape as sand dune, marshes, woods and little villages. A splendid occasion to live in perfect harmony with Nature.
3 years ago -
Fantastic place to visit. You need to get an official tour with the guide, but it is worth it. You can see a lot of different animals in a wildlife. We saw a lot of deers, wild boar, wild horses, many different kind of birds. Unfortunately we didn't see the lynx.
2 years ago -
Lovely sands that stretch for miles. Peaceful unspoilt area. Crossed by ferry from Sanlucar €8 return
2 years ago -
We visited for 2 nights 3 days staying at the Parador at Mazagon. We love nature so this was an ideal location for us. We spent most of our free time visiting the various information centres in the area and enjoying the walks that we could do and the numerous visual displays set up in these centres. For obvious reasons, in order to visit the inner parkland area it is necessary to book ahead and go on an escorted keep ride which lasted 4 hrs. They do it twice daily early morning and late evening avoiding the heat of mid-day.
3 years ago -
Probably the best time to visit is in April May especially if green is your favourite colours as it is mine. The nature, pine trees forests, mixed with eucalyptus and all sort of bushes looks heavenly and the variety of birds and tones on chirps just adds up to this feeric scenary. If you like nature and tracking, here are quite a few extraordinary routes starting with Rociana and El Albaron as well as strolling around the marsh edging El Rocio village, very authentic, pretty eqvestric sceneary, no pavements at all, but definitely fascinating. My son had a ride on a poney, we've been able to watch the flamingos, what more can you wish for ?
2 years ago -
I went on the morning tour to avoid the afternoon heat. The tour guide, Pili, was great explaining interesting things about the park and its flora and fauna. There was a small cold water for each one of us on the bus.
4 years ago -















![Wagon bearing a Simpecado (banner with insignia that proceeds images of the Holy Virgin Mary)[52] crosses the Coto Doñana on its return from the pilgrimage of El Rocío, in May 2009. File:Simpecado_cruzando_el_Coto_de_Doñana,_camino_de_vuelta_de_El_Rocío_IMGP3432.JPG](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/3/37/Simpecado_cruzando_el_Coto_de_Do%C3%B1ana%2C_camino_de_vuelta_de_El_Roc%C3%ADo_IMGP3432.JPG/640px-Simpecado_cruzando_el_Coto_de_Do%C3%B1ana%2C_camino_de_vuelta_de_El_Roc%C3%ADo_IMGP3432.JPG)













































